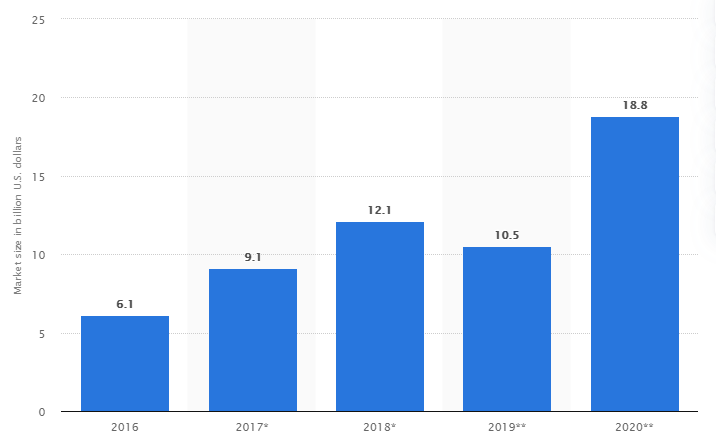
The augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) market amounted to 18.8 billion U.S. dollars in 2020 and is expected to expand dramatically in the coming years.
Source: Statista
Nowadays technology allows you to embody the most unexpected stories: to become a pirate, go virtual shopping, attend a presentation of a prestigious university located across the ocean, or become a Formula-1 participant.
Not all of these scenarios are realistic and interactive indeed, as in our wildest dreams. Nevertheless, they are popular, which allows developers to improve their products. How to create a Virtual Reality application?
Let’s start with a couple of good VR implementation cases.
Contents
Gaming
The easiest way to get to know virtual reality is through video games. For example, according to the monthly report, at the end of 2018, 0.3% of active Steam users owned a VR headset, which amounted to more than 4 million users. In April 2020, the figure was 1.91%. This growth confirms that not only is the supply great, but demand is also not far behind.
Marketing
Many leading brands have already integrated VR into their marketing strategy. For example, The North Face (a company specializing in the manufacture of sportswear, mountain clothing, and travel equipment) offered its customers the opportunity to stroll through Yosemite National Park — of course, in virtual reality.
All this makes it possible to interact with the company’s product playfully and attract customers.
Retail
Car companies fell in love with VR technologies. So the client can consider any model in detail and even immediately go for a test drive. Or another option: using VR for store planning and more efficient product positioning, as Loreal did. The creation of physical prototypes takes a lot of resources compared to a virtual store.
Training
The first to use virtual reality was the military. Modern VR technologies have stepped far ahead of their first timid attempts. Now with virtual reality glasses, the paratroopers are training to land in windy weather and simulate group jumps. With the help of glasses, you can walk around a real warship and learn how to control it during combat operations. Actions honed to automatism in virtual reality can save hundreds and thousands of lives when in reality procrastination would be fatal.
Education
These technologies are also used in education. With the help of the VR-system at the lesson of fine arts, you can virtually walk around the art museum, at the lesson of history — with your own eyes see the real battle, at geography — look at the clouds and fly through the planet.
Health
First of all, VR-technologies are used to train doctors. And this is not only operations where there is no room for an error, but also more prosaic applied tasks: communication with patients, anesthesia, or first aid. Special simulators help get rid of phantom pains for people who have lost limbs and reduce severe pain during burns. They influence the consciousness of patients and thus cure some psychological disorders and alleviate the symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder in veterans.
Tourism
In times of global quarantine, this is perhaps the best way to travel. There is Google Earth VR, which allows you to fly over the planet for free, or Everest VR, which simulates the conquest of the highest mountain in the world, without leaving your living room.
VR development
VR apps are not completely new and unknown technology. Let’s look at the main stages of creating a VR application, as well as the tools, methods, and skills used.
Design and prototype tools
As usual, the VR app development process begins with design. You can skip this step using the community-run libraries. Downloading premade backgrounds or objects also greatly speeds up the process.
Pencil
Even though we work with virtual reality, there are ready-made printed templates that can later be converted into virtual sketches.
Sketch
This mobile interface design tool can easily transform a Sketch document into a 360-degree view prototype.
Blender
It is a popular free open-source modeling and animation tool. Besides, it gives the ability to immerse yourself in your 3D scenes to see them near and on a real scale.
3ds Max and Maya
Autodesk Maya and 3ds Max are two popular 3D computer graphic programs. Though originally released in the 1990s, both software platforms are continuously updated and are in wide use today.
Many impressive VR apps will use 3D computer graphics to simulate immersive worlds – be it underwater, in space, or buildings not yet built. The transformational power of VR allows us to fully experience completely computer fabricated environments.
Cinema 4D
Cinema 4D is the perfect package for all 3D artists who want to achieve breathtaking results fast and hassle-free. This tool is popular among small teams and individual artists and, unlike Autodesk products, is available for Mac OS.
WebVR libraries
WebXR Device API
The WebXR Device API provides access to input (pose information from headset and controllers) and output (hardware display) capabilities commonly associated with Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) devices. It allows you to develop and host VR and AR experiences on the web.
A-Frame
It is a web framework for building virtual reality experiences using HTML. A-Frame can achieve native-like latency and frame rate with proper browsers (e.g., Firefox with WebVR).
React 360
React 360 provides the tools necessary to create high-quality interfaces and delivers a strong foundation for applications built around 360 and 3D content. The techniques and tools used in React 360 are similar to the ones used by Oculus and Facebook when developing their VR applications on mobile and PC platforms and are the result of years of research into best practices.
Primrose
Primrose is a web development framework for building virtual reality experiences in the web browser. It has been used to make 3D chat rooms, billiards games, live-programming environments, and even music sequencers.
Of course, there are many other tools for working with VR, for example, JanusVR, or X3Dom.
Game engines
To develop VR applications, you need a game engine. Game and VR engines are programs specifically designed to create exciting and realistic worlds that require programming and graphic design skills.
Most VR engines let you publish your application on all major platforms. Now we will introduce 3 main ones.
- Unity 3D is a game engine and IDE for cross-platform game development. It is very easy to learn and has a large set of functions for developing games. Unity can create augmented reality apps for Daydream, Cardboard, or Gear VR! It is a pure must-have for VR engineers. This engine uses C# — an object-oriented scripting language — to write commands for game objects and the general logic of your virtual world. One of the biggest advantages of Unity is its huge resource store for free and paid 3D objects, textures, and audio files.
- Unreal Engine is a game engine and an alternative for those interested in cross-platform and full-featured game development. This tool uses the C++ language, which is considered more complex than C# or Java. Unreal is the main competitor for Unity. It also supports all major VR devices. However, in terms of graphics, games on Unreal are far superior to games on Unity.
- CryEngine. Another free tool for creating interfaces. Its peculiarity lies in the exceptional study of weather and water, for example, three-dimensional visualization of clouds. CryEngine also works with C++ and, unlike its competitors, supports only three VR platforms: HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, and OSVR.
It doesn’t matter which engine you choose, as there are no reasons why you cannot give all of them a chance.
Platforms and SDKs
The next issue to solve is the platform choice. Using Unity or Unreal, you can enter any market. But for quality development, you need to choose the starting SDK. The SDK is a plugin that you add to the engine of your choice, which includes resources, content, and methods specific to the engine and platform that form a common native interface for each device. It is logical to start with the brand’s official SDK.
All VR devices on the market can be divided into 2 categories:
- High-end: high-performance products with high technical requirements (HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, and PlayStation VR)
- Mainstream: a device consisting of glasses, and use mobile devices as displays (Samsung Gear VR, Oculus Go, or Google Daydream)
In the following table, you can find a comparison of 6 VR devices of both categories.
| Product | Type | Shipping platform | SDK |
| HTC Vive | PC | Steam VR | Viveport SDK, OpenVR SDK, SteamVR SDK, VRTK |
| Oculus Rift | PC | Steam VR. Oculus | Oculus SDK, Oculus Windows SDK, Oculus Mobile SDK, engine-specific SDKs, VRTK |
| Oculus Go | Standalone | Oculus, Oculus app | Oculus Mobile SDK |
| Samsung Gear VR | Mobile | Oculus | Oculus Mobile SDK |
| Google Cardboard | Mobile | Cardboard app, Google Play Store, YouTube | Google VR SDK |
| Google Daydream | Mobile | Daydream app | Google VR SDK |
Performance testing
The best way to release a product that no one will use is to release it with many bugs. However, if we are talking about VR content, bugs are just the tip of an iceberg. Potential problems that will certainly lead users out of their mental and physical balance are hidden much deeper.
Before testing, issues with software for capturing images and videos should be resolved. At this stage, you can contact a team of dedicated testers.
During testing, attention is drawn to the following:
- Motion sickness and what can cause it: FPS, moving around the stage, impact on the player;
- Camera height;
- Effect of immersion;
- Correct LOD switching and text readability;
- Passable levels, inability to cut the path;
- Interactive objects: throw away key objects and grab everything you can.
In general, VR and non-VR content are very similar for the tester, but without knowing some platform features, you can skip critical shortcomings.
Why do VR applications scare?
Money. VR-headset costs a lot. Besides, new models do not come out often, so there is no stimulus to update devices.
The lack of widespread practical application leads to the fact that virtual reality is recalled more like a toy than a sphere capable of attracting investment.
Technical requirements. Both for use and 3D modeling and VR design, a suitable robust computer costs a lot. This is a problem for both the developer and the consumer.
Usability. Most VR sets are quite heavy and do not at all look like light and compact glasses from our expectations. In addition, a separate room or space is often allocated for their use. Until VR devices become lightweight and mobile, this issue will limit their implementation.
Health. PlayStation and Oculus do not recommend using headphones for children under 13 years old. Pregnant women should first consult a doctor. There are some limitations, which, however, are not much different from those applicable to TV.
Virtual reality applications are a pretty risky venture. However, if within the framework of your business idea this technology is viable, then it’s worth a try. Therefore, if you are interested in testing uncharted territories, there are ways to do this — you just need to choose one of many approaches.
Stay tuned for our new posts!





